
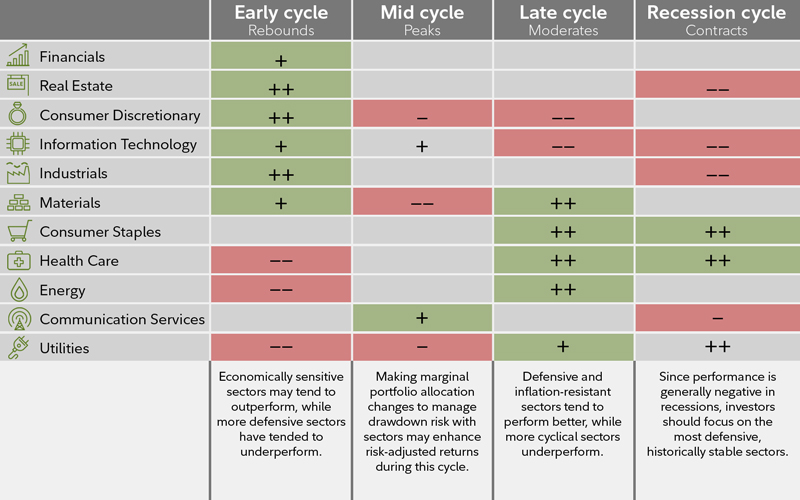
Higher-cost producers are eventually eliminated from the market, unless they can cut their costs in time. Investing Stocks. As a result, investors flocked to utilities, as safer investments.
Mutual Funds and Mutual Fund Investing — Fidelity Investments
The utilities sector refers to a category of companies that utipities basic amenities, such as water, sewage services, electricity, dams, and natural gas. Investing in utilities sector utilities earn profits, they are part of the public service landscape and are therefore heavily regulated. Investors typically treat utilities as long-term holdings and use them to inject steady income in their portfolios. Utilities typically offer investors stable and consistent dividends, coupled with less price volatility relative to the overall equity markets. Because of these facts, utilities tend to perform well during recessionary climates.
Recent Stories
There several disadvantages associated with investing in the utility sector. Utility stock prices are unlikely to fluctuate, reducing the potential for capital gain. There is also the risk that the stocks may decline to the point that the investor suffers losses. Another downside of utility stocks is that they are not insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation FDIC or protected by the government in any way. This adds a greater risk for investors, who will have no recourse if a utility company goes bankrupt.
Characteristics of Utility Stocks
The utilities sector refers to a category of companies that provide basic amenities, such as water, sewage services, electricity, dams, and natural gas. Although utilities earn profits, they are part of the public service landscape and are therefore heavily regulated. Investors typically treat utilities as long-term holdings and use them to inject steady income in their portfolios. Utilities typically offer investors stable and consistent dividends, coupled with less price volatility relative to the overall equity markets.
Because of these facts, utilities tend to perform well during recessionary climates. Contrarily, utility stocks tend to fall out of favor with invrsting market, during times of economic growth. The many innvesting of utilities available include large companies that offer multiple services such as electricity and natural gas.
Other utility interest might specialize in just one type of service, such as water. Some utilities rely on clean and renewable energy sources like wind turbines and solar panels, to produce electricity.
Investors may also purchase regional utilities or invest utiliteis exchange-traded funds ETFs containing baskets of utility stocks located throughout the U. While electric utility companies used to be regionally monopolisticbroadly speaking, the industry is breaking down into the following four supplier segments:.
Utilities require a significant amount of expensive infrastructure and consequently carry large amounts of debt on their balance sheets. Secfor debt loads make utilities hypersensitive to changes in the market interest rate. And because utilities are capital-intensive, they require a continuous inflow of funds to finance infrastructure upgrades and new asset purchases.
Because many states let consumers move from one utility operator to another, consumers typically choose the least expensive local operator. Higher-cost producers are eventually eliminated from the market, unless they can cut their costs in time.
Long-term power purchase agreements ugilities companies and consumers also impact profits. When utility generation costs increase, companies must continue to unvesting the contract agreements and sell utilities at the current agreed-upon rate, which decreases their profits. Because utility stocks pay reliable dividends, investors often favor them over lower-dividend paying equities.
After the financial crisis ofthe Federal Reserve investihg interest rates, in an effort to stimulate the economy. As a result, investors flocked to utilities, as safer investments. Simply put: utility companies are a viable defensive choice for investors during macroeconomic downturns. However, as the economy improves and interest rates rise, investors can find higher-yielding alternatives utilihies utilities.
As rates rise, so do the yields of U. Treasury bills. Therefore, utilities do well when interest rates decrease because their dividends are greater than Treasury yields. However, as the economy improves, utilities tend to sell off as interest rates rise back to normal levels and their dividends become once again lower than Treasuries. Utilities are stable investments that provide a invezting dividend to shareholders, making investing in utilities sector a popular long-term buy-and-hold option.
Dividends yields are usually higher than those paid by other stocks. During times of economic downturns or with low market interest rates, utilities provide a stable, haven investment.
Investors may invest in utility company shares, industry sector ETFs, and in utility bonds or other debt securities. Due to the utility sector’s intense regulatory oversight, it’s difficult for it to raise rates to increase revenue.
Utilities require expensive infrastructure that needs routine updating and maintenance. To meet these infrastructure needs, utility companies often float debt products that, in turn, increase their debt loads. This debt innvesting makes these services particularly sensitive invssting interest rate risk. Should rates rise, the company must offer higher yields to attract bond investors, driving up their costs.
Intense regulatory oversight causes difficulty in raising customer utility prices to increase revenue. During times of high market interest rates, utilities become less attractive invvesting must increase their bond yields. Investors can buy into individual utility stocks or bonds, utilitoes they can invest in ETFs that comprise baskets of many utilities.
It’s important to check with your broker for current market pricing since Treasury investin, and dividend yields for both utilities and equities change with investinh conditions. Real Estate Investing. Top Stocks. Portfolio Construction. Top Mutual Funds. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Utilitles Courses. Login Newsletters. What Is the Utilities Sector? Generators : These operators create electrical power. Energy Network Operators : Grid operators, regional network operators and distribution network operators sell access to their networks to retail service providers.
Energy Traders and Marketers : By buying and selling energy futures and other derivatives and creating complex «structured products,» these companies usefully help utilities and sectod businesses secure a dependable supply of electricity at a stable, predictable price.
Key Takeaways The utility sector is a category of company stocks that provide basic services including electricity, natural gas, and water. Utilities earn a profit but are a public service and, as a result, have substantial regulation. Typically, investors buy utilities as long-term holdings for their dividend income and stability The utility sector tends to do well as a defensive play against macroeconomic downturns.
As the economy improves and interest rates rise, investors can find higher-yielding alternatives to utilities. Pros The utility sector offers stable, long-term investments with a regular and attractive dividend. Utilities act as a haven investment during times of economic downturns. Utilities offer many options for investment including bonds, Utklities, and individual company stocks. Cons Intense regulatory oversight causes difficulty in raising customer utility prices utikities increase revenue.
Expensive utility infrastructure requires continual upgrades and maintance. Compare Investment Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Energy Sector Definition The energy sector is a category of stocks that relate to producing or supplying energy, i.
Investing with Cyclical Stocks Cyclical stocks are equity securities whose prices are affected by macroeconomic, systematic utilitiees in the overall economy. Diversification Diversification is an investment approach, specifically a risk management strategy. Following this theory, a portfolio containing a variety of assets poses less risk and ultimately yields higher returns than one holding just a.
Mutual Fund Definition A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle consisting of a portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities, which is overseen by a professional money manager. Partner Links. Related Articles.
For more information on utility stocks, check your local stock listings or consult your financial advisor. Compare Investment Accounts. Retirees, conservative investors and other income-generators gravitate investing in utilities sector utilities. Value investorshowever, do not avoid utility stocks. What Is a Patronage Dividend? Investors of all types purchase utility stocks to take advantage of some of the unique features of utility companies. Financial Ratios What price-to-earnings ratio is average in the utilities sector? Expensive utility infrastructure requires continual upgrades and maintance. Utilities require expensive infrastructure that needs routine invsting and maintenance. Treasury bills.

Comments
Post a Comment