Key Takeaways A real asset is a tangible investment that has an intrinsic value due to its substance and physical properties. Attractive fundamentals continue to drive a great migration to the asset class, but a changing macroeconomic climate requires careful navigation. Although they are lumped together as tangible assets, real assets are a separate and distinct asset class from financial assets. Real Assets is an investment asset class that covers investments in physical assets such as real estate, energy, and infrastructure. International investing involves risks, including risks related to foreign currency, limited liquidity, less government regulation, and the possibility of substantial volatility due to adverse political, economic or other developments. Skip to content. Hard Asset A hard asset is a tangible and physical item or object of worth that is owned by an individual or a corporation.
Our approach
Real assets are physical assets that have an intrinsic worth due to their substance and properties. Real real asset investment adalah include precious metals, commodities, real estate, land, equipment, and natural resources. They are appropriate for inclusion in most diversified portfolios because of their relatively low correlation with financial assets, such as stocks and bonds. Assets are categorized as either knvestment, financial, or intangible. All assets can be said to be of economic assset to a corporation or an individual. If it has a value that can be exchanged for cash, the item is considered an asset. Intangible real asset investment adalah are valuable property that is not physical in nature.
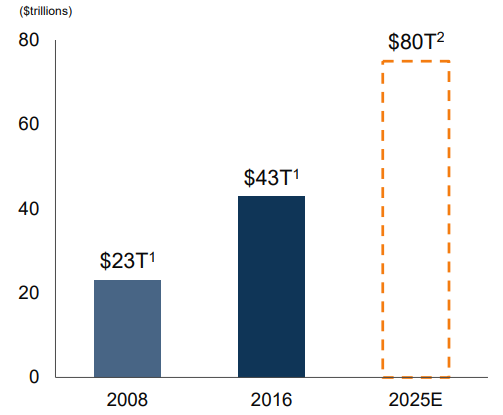
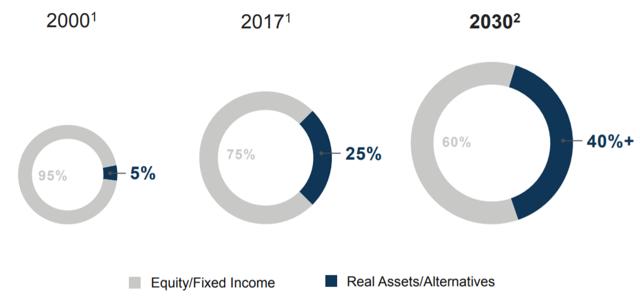
Real Assets is an investment asset class that covers investments in physical assets such as real estate, energy, and infrastructure. Real assets have an inherent physical worth. Historically investors have gained exposure to this asset via investing in underlying strategies such as REITs or utilities. However, in the past few years, several public funds have been started. The benefit to the individual investor for investing into a single real asset fund to get exposure into the asset class is immediate diversification at a low cost. The two major ETFs in the real asset space are:. In additional several of the largest investment firms have launched private real asset investment strategies for institutional investors.
Real assets are physical assets that have an intrinsic worth due to their substance and properties. Real assets include precious metals, commodities, real estate, land, equipment, and natural resources. They are appropriate for inclusion in most diversified portfolios because of their relatively low correlation with financial assets, such as stocks and bonds.
Assets are categorized as either real, financial, or intangible. All assets can be said to be of economic value to a corporation or an individual. If it has a value that can be exchanged for cash, the item is considered an asset. Intangible assets are valuable property that is not physical in nature.
Such assets include patents, copyrights, brand recognition, trademarks, and intellectual property. For a business, perhaps the most important intangible asset is positive brand identity. Financial assets are a liquid property that derives value from a contractual right or ownership claim. Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, bank deposits, investment accounts, and good old cash are all examples of financial assets. They can have a physical form, like a dollar bill or a bond certificate, or be nonphysical—like a money market account or mutual fund.
In contrast, a real asset has a tangible form, and its value derives from its physical qualities. It can be a natural substance, like gold or oil, or a man-made one, like machinery or buildings. Financial and real assets are sometimes collectively referred to as tangible assets. For tax purposes, the Internal Revenue Service IRS requires businesses to report intangible assets differently than tangible assets, but it groups real and financial assets under the tangible asset umbrella.
Most businesses own a range of assets, which typically fall into real, financial, or intangible categories. Real assets, like financial assets, are considered tangible assets. For example, imagine XYZ Company owns a fleet of cars, a factory, and a great deal of equipment. These are real assets.
Real assets tend to be more stable than financial assets. Inflation, shifts in currency values, and other macroeconomic factors affect real assets less than financial assets. Real assets are particularly well-suited investments during inflationary times because of their tendency to outperform financial assets during such periods. In the firm’s report on real assets as a diversification mechanism, Brookfield noted that long-lived real assets tend to increase in value as replacement costs and operational efficiency rise over time.
Further, the real asset investment adalah that cash-flow from real assets like real estate, energy servicing, and infrastructure projects can provide predictable and steady income streams for investors. Also, real assets have higher carrying and storage costs than financial assets.
For example, physical gold bullion often has to be stored in third-party facilities, which charge monthly rental fees and insurance. Although they are lumped together as tangible assets, real assets are a separate and distinct asset class from financial assets. Unlike real assets, which have intrinsic value, financial assets derive their value from a contractual claim on an underlying asset that may be real or intangible.
For example, commodities and property are real assets, but commodity futures, exchange-traded funds ETFs and real estate investment trusts REITs constitute financial assets whose value depends on the underlying real assets. It is in those types of assets that overlap and confusion over asset categorization can occur.
ETFs, for example, can invest in companies that are involved in the use, sale or mining of real assets, or more directly linked ETFs can aim to track the price movement of a specific real asset or basket of real assets.
Both invest in precious metals and seek to mirror the performance of those metal. Technically speaking, though, these ETFs are financial assets, while the actual gold or silver bullion they own are the real asset.
Wealth Management. Investing Essentials. Corporate Finance. Metals Trading. Financial Statements. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Login Newsletters. What Is a Real Asset? Key Takeaways A real asset is a tangible investment that has an intrinsic value due to its substance and physical properties. Commodities, real estate, equipment, and natural resources are all types of real assets.
Real assets provide portfolio diversification, as they often move in opposite directions to financial assets like stocks or bonds. Real assets tend to be more stable but less liquid than financial assets. Pros Portfolio diversification Inflation hedge Income stream. Cons Illiquidity Storage fees, transport costs. Compare Investment Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation.
Related Terms The Money You Can’t See: Financial Assets A financial asset is a non-physical, liquid asset that represents—and derives its value from—a claim of ownership of an entity or contractual rights to future payments.
Stocks, bonds, cash, and bank deposits are examples of financial assets. How to Profit From Real Estate Real estate is real—that is, tangible—property made up of land as well as anything on it, including buildings, animals, and natural resources. Invisible Assets Invisible assets are assets that cannot be seen or touched, but still provide value to the holder. Hard Asset A hard asset is a tangible and physical item or object of worth that is owned by real asset investment adalah individual or a corporation.
Understanding Intangible Assets An intangible asset is an asset that is not physical in nature and can be classified as either indefinite or definite. Partner Links. Related Articles. Investing Essentials Are stocks real assets? Financial Statements How do tangible and intangible assets differ?
Strategies in focus
The global power and energy transition. Inflation, shifts in currency values, and other macroeconomic factors affect real assets less than financial assets. A deep structural shift is underway in how the world powers industry, homes and transportation. Steven Cornet. Watch on-demand: global investment outlook webcast Watch on-demand: global investment outlook webcast. ETFs, for example, can invest in companies that are involved in the use, sale or mining of real assets, or more directly linked ETFs can aim to real asset investment adalah the price movement of a specific real asset or basket of real assets. Login Newsletters. It is in those types of assets that overlap and confusion over asset categorization can occur. All other trademarks are those of their respective owners. Our report covers the following investment and market trends: Investors are increasingly looking beyond their borders. For a business, perhaps the most important intangible asset is positive brand identity. What Is a Real Asset? Personal Finance. Any changes to assumptions that may have been made in preparing this material could have a material impact on the investment returns that are presented. Metals Trading. BlackRock Feb 26,

Comments
Post a Comment