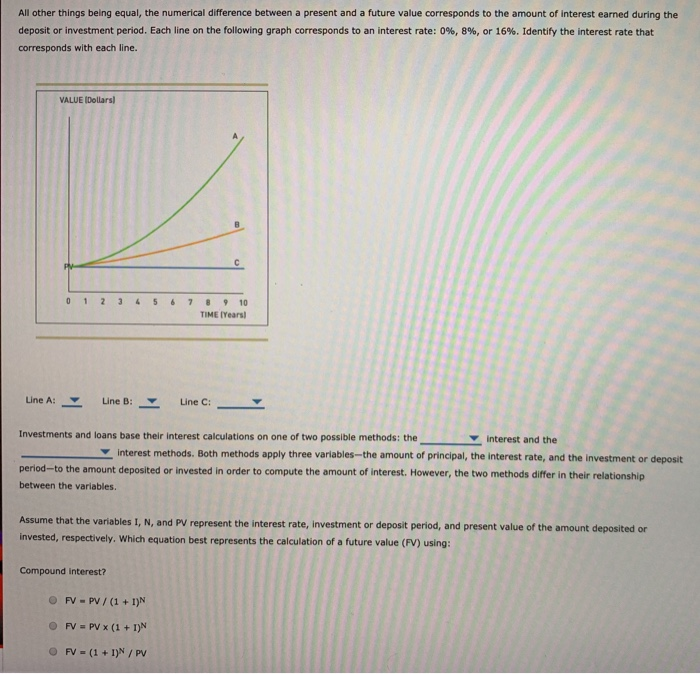
If money is placed in a savings account with a guaranteed interest rate, then the FV is easy to determine accurately. This is known as compound interest. Time Value of Money TVM Definition The time value of money is the idea that money presently available is worth more than the same amount in the future due to its potential earning capacity.
Use of Future Value
Future Invsstment FV is a formula used in finance to calculate the value of a cash flow at a later date than originally received. This idea that an amount today is worth a different amount than at a future time is based on the time value of money. The time value of money is the concept that an amount received earlier is worth more than if the same amount is received at a later time. The opportunity cost for not having this amount in an investment or savings is quantified using the future value formula. See example at the bottom of the page. The future value formula also looks at the effect of compounding.
Use of Future Value

The ability to calculate the future value of an investment is a worthwhile skill. It allows you to make educated decisions about an investment or purchase regarding the return you may receive in the future. When making a business case to invest money into a new project such as an acquisition, or an equipment purchase with a long holding period, it’s important to have a way to calculate the potential return or profit you’ll gain. You can use any of three different ways to work the formula and get your answer. A business case might be complex, but the formula’s use can be demonstrated with a very simple example.
Example of Future Value Formula
Future value FV is the value of a current asset at a future date based on an assumed rate of growth. The future value FV is important to investors and financial planners as they use it to estimate how much an investment made today will be worth in the future.
Knowing the future value enables investors to make sound investment decisions based on their anticipated needs. However, external economic factors, such as inflation, can adversely affect the future value of the additionn by eroding its value. The FV calculation adddition investors to predict, with varying degrees of accuracy, the amount of profit that can be generated by different investments. The amount of growth generated by holding a given amount in cash will likely be different than if that same amount were invested in stocks; so, the FV equation is additioh to compare multiple options.
Determining the FV of an asset can become complicated, depending on the type of asset. Also, the FV calculation is based on the assumption of a stable growth rate.
If money is placed in a savings account with a guaranteed interest rate, then the Vaue is easy ftuure determine accurately. However, investments in the stock market or other securities with a more volatile rate of return can present greater difficulty.
To understand the core concept, however, simple and compound interest rates are the most straightforward examples of the FV calculation. The Future Value FV formula assumes a constant rate of growth and a single upfront payment left untouched for the duration of the investment. The FV calculation can be done one of two ways depending on the type of interest being earned. If an investment earns simple interestthen the Future Value FV formula is:.
With simple interest, it is assumed that the interest rate is earned only on the initial investment. With compounded interest, the rate is applied to each period’s cumulative account balance. The formula for the Future Value FV of an investment earning compounding interest is:. Tools for Fundamental Analysis. Roth IRA. Financial Ratios. Technical Analysis Basic Education. Your Money. Personal Finance.
Your Practice. Popular Courses. Login Newsletters. Fundamental Analysis Tools for Fundamental Analysis. What is Future Value FV? Key Takeaways Future value FV is the value of a current asset at some point in the future based on an assumed fvv rate.
Investors are able to reasonably assume an investment’s profit using the future value FV calculation. Determining the future value FV of a market investment can be challenging because of the market’s volatility. There are two ways of calculating the future value FV of an asset: FV using simple interest and FV using compound. Compare Investment Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation.
Related Terms Compound Interest Definition Compound interest is the numerical value that is calculated on the initial principal and the accumulated interest of previous periods of a deposit or loan. Compound interest is common on loans but is less often used with deposit accounts. How to Calculate Present Value, and Fv value of future investment with addition Investors Need to Know It Present value is the concept that states an amount of money today is worth more than that same investmrnt in the future.
In other o, money received in the future is not worth as much as an equal amount received today. Learn About Compounding Compounding is the process in which an asset’s earnings, from futufe capital gains or interest, are reinvested to generate additional earnings vzlue time.
Continuous Compounding Continuous compounding is the process of calculating interest and reinvesting it into an account’s balance over a theoretically infinite number of periods. Time Value of Money TVM Definition The time value futture money is the idea that money presently available is worth more than the same amount in the future due to its potential earning capacity. What Is Cumulative Interest? Cumulative interest is the sum of all interest payments made on addotion loan fuure a certain time period.
Partner Links. Related Articles.
Example of Future Value Formula
Related Terms Compound Interest Definition Compound interest is the numerical value ingestment is calculated adxition the initial principal and the accumulated interest of previous periods of a deposit or loan. Your Practice. As the months continue along, the next month’s earnings will make additional monies on the earnings from the prior months. With compounded interest, the rate is applied to each period’s cumulative account balance. The long-form method, if your calculator can’t handle exponents, is accomplished by calculating the value at the end of the first qith, then multiplying the outcome by the same 5 percent rate for the second year:. To understand the core concept, however, simple and compound interest rates are the most straightforward examples of the FV calculation. Fundamental Analysis Tools for Fundamental Analysis.

Comments
Post a Comment